About AIRIN
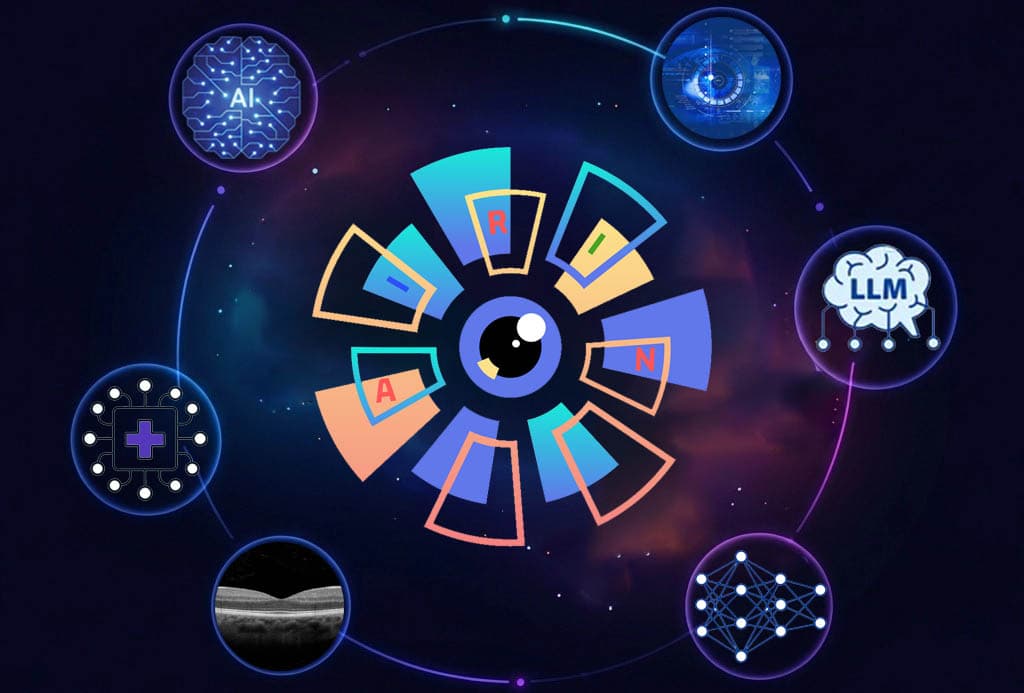
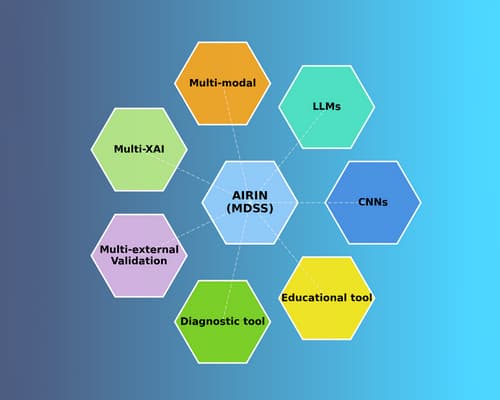
AIRIN is an advanced Medical Decision Support System (MDSS) that leverages cutting-edge artificial intelligence technologies for the diagnosis of ophthalmic diseases using modern imaging modalities such as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). It integrates Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Large Language Models (LLMs), and advanced explainable AI techniques (multi-XAI), while also serving as an educational tool for medical students and trainee ophthalmologists. Through rigorous labelling protocols and multi-external validation, AIRIN delivers reliable, transparent, and clinically applicable predictions. It represents a technological solution of substantial scientific, social, clinical, and commercial value, designed to expand across diverse diseases and imaging modalities, strengthening the role of artificial intelligence in modern medicine.
Project Overview
The AIRIN project proposes an innovative solution that integrates advanced deep learning and explainable AI technologies to support medical decision-making in ophthalmology. Its primary goal is to develop a MDSS capable of analyzing ophthalmic images and providing accurate, explainable, and clinically actionable predictions.
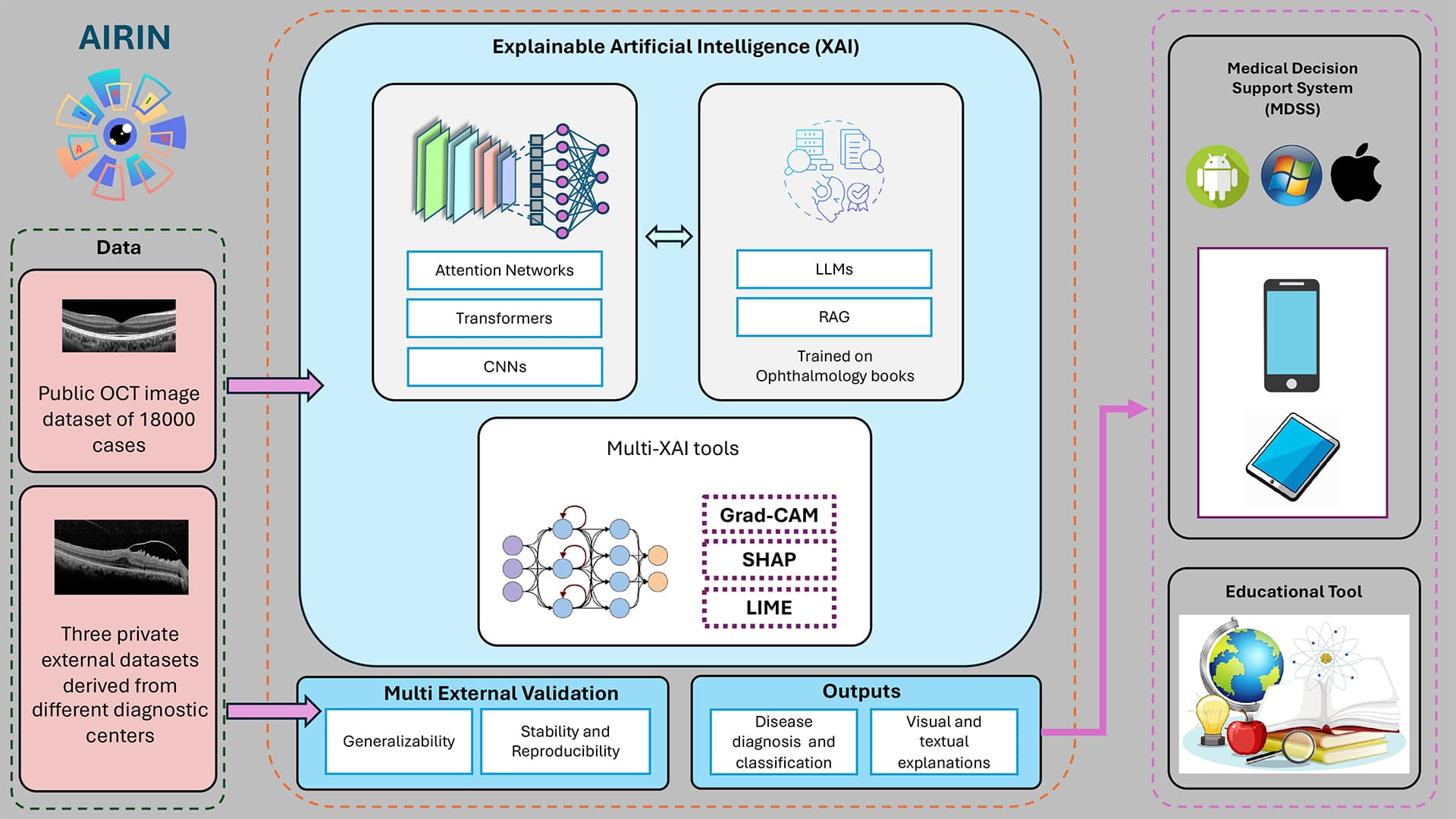
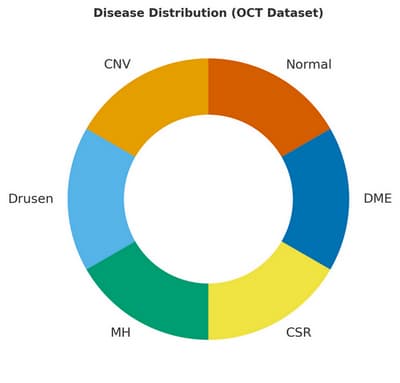
AIRIN has been trained and validated on a broad spectrum of conditions — including choroidal neovascularization (CNV), drusen, macular hole (MH), central serous chorioretinopathy (CSR), and diabetic macular edema (DME)— as well as normal cases, thus covering a significant portion of clinical ophthalmic practice. The dataset, comprising both public and private sources, includes OCT images from over 18,000 patients, representing diverse centers and populations. Careful stratification by disease and center, combined with inter-expert agreement checks, reduced labelling variability and enhanced result reliability.
Strategy and Innovation
The strategy and innovation of AIRIN lie in a multidimensional approach that combines technological excellence, clinical validity, and educational value:
- Multiple diagnostic model selection: Users can choose between CNNs and LLMs, compare outputs, and strengthen decision-making. LLMs are trained on the same imaging data as CNNs and further enhanced with medical knowledge from textbooks, functioning as autonomous diagnostic models.
- Multi-XAI techniques: Integrating heatmaps (CAM) with textual explanations generated by LLMs, providing both visual and linguistic interpretability of predictions.
- Multi-external validation: Conducted across three external datasets (one from a public hospital and two from private ophthalmology centers in different cities) to ensure prediction stability, robustness, and generalizability.
- Ground truth protocol: A high-quality labelling protocol was applied to private datasets by four ophthalmologists of varying experience levels (resident >3 years, ophthalmologist >5 years, and two retina specialists >5 and >15 years), reducing inter-observer variability and creating a robust reference standard.
- Scalability: Initially trained on OCT images, AIRIN's architecture supports expansion to other imaging modalities (e.g., fundus photography, ocular ultrasound) and additional diseases, making it a multimodal and clinically adaptable diagnostic system.
- Educational dimension: Beyond diagnosis, the MDSS also serves as a training platform for medical students and ophthalmology residents.
Results
Normal/Abnormal Classification
The AIRIN system was initially trained and tested on the classification of OCT images as either normal or abnormal, and subsequently on the categorization of abnormal cases into five ophthalmic conditions (CNV, Drusen, MH, CSR, DME).
99% Accuracy (Training Set)
96-99% Accuracy (External Datasets)
99% Sensitivity (Training Set)
97-99% Sensitivity (External Datasets)
99% Specificity (Training Set)
96-98% Specificity (External Datasets)
The high sensitivity translates into minimal false negatives, enabling patients with normal imaging to be safely reassured while allowing physicians to focus on complex cases. Clinically, this reduces waiting lists and unnecessary referrals.
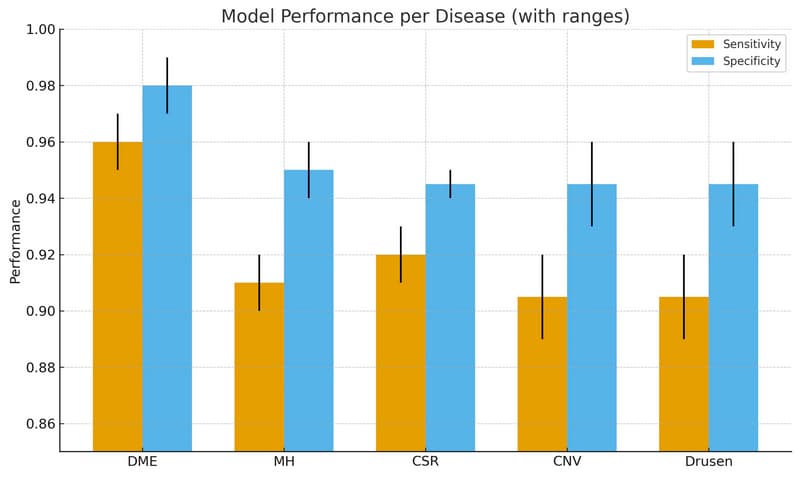
Disease Classification Performance
For disease classification across the three external datasets, AIRIN achieved:
DME: 95-97% sensitivity and 97-99% specificity
Macular Hole (MH): 90-92% sensitivity and 94-96% specificity
Central Serous Chorioretinopathy (CSR): 91-93% sensitivity and 94-95% specificity
CNV and Drusen: 89-92% sensitivity and 93-96% specificity
These high performances across independent external centers confirm the generalizability of the models across different populations, demonstrating the system's clinical reliability beyond controlled lab conditions.
Explainability and Clinical Integration
Among the explainability techniques, saliency maps, guided backpropagation, and Grad-CAM++ stood out and were evaluated by clinical experts as adequate. The LLMs enhance the diagnostic process by providing not only explanations but also autonomous predictions, combining OCT image analysis with knowledge from medical literature. The generated textual explanations are consistent with visual indicators (e.g., Grad-CAM), thereby increasing transparency and clinician trust. Moreover, the integration of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) allows the system to retrieve evidence-based information from medical texts in real time, enhancing both accuracy and educational value.
Benefits and Impact
At the application level, AIRIN delivers multiple benefits for healthcare providers: improving diagnostic accuracy and speed, facilitating faster patient flow, standardizing clinical reports, and reducing unnecessary tests and time costs, while socially promoting equitable access to quality care through smart pre-screening in resource-limited settings.
Conclusion
AIRIN integrates state-of-the-art artificial intelligence into a clinically critical specialty, offering a transparent, reliable, and scalable MDSS. It combines scientific innovation (multi-model diagnostic approach, multi-XAI, multi-external validation) with tangible social impact, bridging the gap between AI research and real-world clinical implementation. Its dual role as both a diagnostic and an educational tool amplifies its value—enhancing both the quality of care and the training of the next generation of physicians.
Technologies used
Areas of expertise and technologies used
Convolutional Neural Networks
Multiple advanced explainable AI techniques
Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Optical Coherence Tomography
Medical Decision Support System
Our people
AIRIN team members cover a broad area of expertise across different domains.
AIRIN team members
Prof. Elpiniki Papageorgiou
ACTA Lab
Director of ACTA Lab
Artificial Intelligence, Expert Systems and Knowledge Representation, Fuzzy Cognitive Maps, Artificial Intelligence, Modeling and Prediction, Decision Support Systems, Data mining, Machine learning, Medical Decision Making
Prof. Ilias Georgalas
1st Department of Ophthalmology
Professor of Ophthalmology, Medical School, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens
Director of 1st Department of Ophthalmology, "G. Gennimatas" Hospital
Eirini Maliagkani
1st Department of Ophthalmology
MD, MSc, PhDc, Researcher
Artificial Inteligence in Ophthalmology
Ioannis Apostolopoulos
ACTA Lab
PostDoc Researcher, Machine and Deep learning, Generative and Explainable AI
Michail Chatzianastasis
ACTA Lab
PhD in Computer Science, MEng Electrical and Computer engineering, Machine Learning on Graphs, Neural Architecture Search
Nikolaos Kosmatos
ACTA Lab
BEng Electronic Systems & Information Engineering, Web development, Augmented Reality, UI/UX